 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The 1899/1900 FN Browning by Ed Buffaloe Historical Perspective Guncotton, or nitrocellulose, made by dipping cotton in a mixture of nitric and sulfuric acids, was patented in 1846 by a Swiss chemist by the name of Christian Friedrich Schönbein, based on earlier work by French chemists Henry Braconnot and Théophile-Jules Pelouze. Guncotton is highly flammable and chemically unstable, so early efforts to utilize it as a gunpowder ingredient or explosive caused some serious disasters. But in 1884 the French chemist Paul Marie Eugène Vieille found a way to stabilize it. He called his invention poudre blanche, or white powder, to distinguish it from traditional black gunpowder. It burns much faster than black powder and produces comparatively little smoke, so it quickly became known as “smokeless” powder. A number of attempts to create a self-loading (automatic) weapon were made prior to the invention of smokeless powder, including a gas-operated revolver made by Orbea Hermanos of Eibar, Spain as early as 1863. None of these efforts were ultimately viable because of the heavy residues left by black powder, which inhibits mechanical functioning very quickly. But immediately after the invention of smokeless powder, a number of people began serious work on designs for self-loading guns. The most significant successful designs (other than John Browning’s) were those by Mannlicher, Bergmann, and Mauser. Most of these early self-loading pistols had limited sales and/or were intended primarily for military use. John Moses Browning (1855-1926) grew up in his father’s gun shop and learned to repair guns before he learned to read and write. He filed his first firearm patent in 1879 at the age of 24. Browning began experimenting with self-loading weapon designs late in 1889. He filed a patent on a gas-operated machine gun on 6 January 1890, and followed it with another dozen or so patents over the next decade on various types of self-loading weapons, both gas and recoil operated. By 1894 Browning had completed his first prototype automatic pistol. In 1895 the Colt’s Patent Fire Arms Manufacturing Company began producing one of Browning’s machine gun designs, which marked the beginning of a long collaboration between John Browning and the Colt’s Company. On 24 July 1896 Browning signed a contract giving Colt’s the right to manufacture four of his automatic pistol designs for distribution in the U.S. and Canada. However, Colt’s was almost certainly acquiring the rights in order to protect sales of their revolvers. There was, as yet, no established market for self-loading pistols in the U.S.
Browning was granted U.S. patent 621,747 on 21 March 1899, covering the final design for the 1899/1900 FN Browning. Connecticut had been an early center for the manufacture of brass hardware, clocks, and firearms--and later of machine tools, gauges, bicycles, sewing machines, and all manner of precision mechanical devices. Firearms manufacture was particularly centered in Hartford and New Haven, which both had rivers to provide power for machinery. In the late ninteenth century, Connecticut, and the Colt’s factory at Hartford in particular, was a major center for the dissemination of information and knowhow on the manufacture of interchangeable parts, which had become known in Europe as “the American System” of manufacture. In 1893, when Browning was in Hartford to demonstrate his machine gun, he met a Colt engineer by the name of Hart O. Berg. Berg was a native of Philadelphia, but his parents were immigrants, and he grew up speaking both German and English. He studied engineering in Liège, Belgium between 1884 and 1891, where he also became fluent in French. Berg and Browning became friends and corresponded by letter when Browning was not in Hartford. This correspondence continued when Berg moved back to Liège and went to work for Fabrique Nationale (FN). Several times in 1896 and 1897 Berg asked Browning to come to Liège and show some of his inventions to FN. So, on 31 March 1897, Browning took ship for Europe with his prototype blowback pistol and 500 rounds of ammunition. Colt’s had contracted in 1896 to manufacture Browning’s handgun designs in the U.S., but actual production was still a long way off, and in any case Colt’s had not purchased Browning’s blowback-operated designs, preferring instead to concentrate on locked-breech guns suitable for military applications. So Browning wasn’t doing anything devious; he was simply trying to get his favorite little pistol into production any way he could. The FN engineers were astonished when Browning’s hand-made prototype fired 500 rounds without a single failure to feed or eject. There probably wasn’t another self-loading pistol in the world as reliable. Browning signed a contract with FN on 17 July 1897 to manufacture and sell the pistol in most of Europe. The contract specifically forbade the sale of the gun in the U.S. and Canada, where Colt’s had the right to sell Browning’s designs, which is probably the main reason these guns are relatively scarce in the U.S. today, especially the Model 1899. According to Vanderlinden, Hart Berg traveled to Ogden, Utah in January of 1898 to try to convice John Browning to come to Belgium and supervise the tooling-up process for manufacturing the pistol. But Browning was in the most creative phase of his life and had other priorities. Instead, he gave Berg his recommendations on how he thought the pistol could be most efficiently produced .* FN began tooling up immediately, and the first prototypes were ready for testing by July. The first production guns went on sale in January of 1899. The 7.65mm Browning Cartridge According to W.H.B. Smith, the 7.65mm Browning (.32 auto) cartridge was developed from the 8mm Bergmann Simplex cartridge, however this seems unlikely since the Simplex probably didn’t appear until at least 1900. Hogg & Walter state it didn’t appear until 1902, in which case the Simplex cartridge might just as well be based on the Browning. The Bergmann cartridge had a slightly tapered case that was about 5 thousandths of an inch longer than the Browning, and a bullet of nearly identical weight, though the Simplex cartridge generated a lower muzzle velocity. Both guns were blowback-operated. The Ammo Encyclopedia says the .32 auto cartridge was developed in 1897, the year of the initial patent. Henry White and Burton Munhall in their book Pistol and Revolver Cartridges state: “Recent research leads us to believe that the cartridge may have been developed experimentally in this country, although it was first introduced in Belgium in 1900 [sic] by Fabrique Nationale with the advent of the Browning Automatic Pistol. We know that Browning patented his gun in 1897 and that for the next few years considerable work was done by various American companies on cartridges for his weapon.” They cite a .32 Browning Automatic cartridge that was listed in the Winchester Repeating Arms Company catalog for August 1899. They examined one of these cartridges which was headstamped “W.R.A.Co. .32 B.A.” and had a soft lead bullet. John Malloy, in his article “Early Auto Pistol Cartridges,” doubts that Browning ever had the opportunity to examine a Bergmann Simplex cartridge. He establishes that Browning had a longstanding relationship with Winchester, that the Browning brothers’ store carried Winchester cartridges, a number of which were in .32 caliber, and that Browning’s machine guns were all made to shoot existing rimmed rifle cartridges. Malloy believes that Browning started with an existing .32 cartridge: “It seems plausible that Browning shortened some of these [cartridges] to a case length he felt to be suitable for a magazine inside the grip. He would then have reduced the rim until the cartridges fed smoothly over each other, leaving a slight flange to position the round in the chamber. The semi-rimmed pistol cartridge was probably born in this manner.” Anthony Vanderlinden, in FN Browning Pistols, Side-Arms that Shaped World History, reproduces a photograph of a box of 7.65mm FN cartridges that clearly shows a drawing of a Model 1899 pistol on the label. FN 7.65mm cartridges were available for sale when the pistol went on the market in January of 1899. The Model of 1899
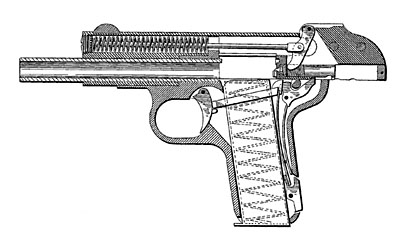
The Model 1899 is a striker-fired weapon which consists of a frame with a barrel screwed into it, a slide, and a separate breech block. It was the first pistol ever to have a reciprocating slide as opposed to a reciprocating breech block or bolt. The slide fits onto the frame from the front, while the breech block is inserted from the rear; the two are joined by two large screws. The lower front portion of the slide completely surrounds the barrel, behind which is the attached breech block, slotted into the rear of the frame. The upper portion of the slide consists of a tunnel enclosing the recoil spring, which does double duty as the striker spring. There is an ejection port on the right side of the frame. The extractor is a piece of spring steel with a hook on the end. The gun features a stirrup-shaped transfer bar, the two sides of which run from the trigger to the sear on either side of the magazine. The sear is tensioned by a leaf spring in the grip of the gun, behind the magazine. The manual safety blocks the sear and locks the trigger. There is no provision for locking the slide open for cleaning. Due to the weight of the slide and breech block, the gun has remarkably little felt recoil. Its fixed barrel and precision manufacture (à la FN) make it extremely accurate.
In 1899 the Belgian army was looking for a self-loading pistol. They tested all the pistols of the era: the Mauser, the Bergmann, the Roth (I presume this was a prototype Roth-Steyr), the Mannlicher, the Borchardt, and the Borchardt-Luger. Probably immediately after the first Belgian army pistol trials FN decided to make a larger version of the M1899. I’m guessing the little pistol looked positively diminutive next to the other guns in the trials, and FN thought it might be better received if it were larger. The larger version had an extended grip, frame, and slide. According to Vanderlinden, its overall length was 184mm (7.25 inches), its barrel length was 122mm (4.8 inches), and it held 8 rounds instead of 7. Only a very small number of these large models were made. Gangarosa incorrectly gives the measurements and capacity of the large test model in place of those for the Model 1899. The large gun was entered into subsequent Belgian military trials toward the middle of 1899. The standard model and the large model were both entered in the British military trials in December of 1900, but were rejected due to the inadequate power of the 7.65mm Browning cartridge.
One of the distinctive features of these pistols is the reinforced area of the frame above the trigger guard, which is made of thicker steel than the rest of the frame. On the Model 1899, this area extends just beyond the middle of the trigger guard (to the top front of the trigger itself), and the rear line of this reinforced area slants toward the front of the gun. This reinforced area of the frame is marked on the left side Breveté S.G.D.G. (indicating the gun is patented), and is stamped with an oval cartouche featuring an image of the gun with a small FN monogram beneath it. Some early safety levers have a round grip area with three concentric circles, while others are checkered. There are no markings to indicate which position is ‘Fire’ and which is ‘Safe.’ The hard rubber grip plates feature an oval cartouche at the top with a picture of the gun and the FN monogram. Beneath the oval, the grip plates are checkered. The grip plates are quite thin and small, leaving several millimeters of steel grip area on the sides. There is 4 or 5 millimeters of metal grip uncovered beneath the bottom of the grip plates. The grip plates are held on by a large round plate in the rear with a threaded stud protruding through the grip plate onto which is screwed a slotted nut.
The finish was rust blue, with a fire blued trigger. Nickel plating was an option, but few specimens are known with factory nickel. No engraving was offered for the M1899. Only a single fancy engraved model is known from the production era--a gun presented by FN to Theodore Roosevelt. The Model of 1900
The grip plates are thicker than those on the M1899 and extend almost to the edges of the grip frame. Some early military contract guns were delivered with plain checkered grip plates that did not feature the oval cartouche at the top--these are quite scarce today. Many of these grips were later replaced by plain checkered wooden grips, which are also quite scarce today. The commercial grip plates continued to have the oval cartouche at the top with a picture of the gun and the FN monogram until 1905. The left grip plate has a cutout on one corner where it abuts the lanyard. At around serial number 200,000 the grip design was changed--the grips were slightly smaller (leaving a couple of millimeters of grip frame showing around their edges) and the oval cartouche contained only the large FN monogram. The grip plates are retained by a rectangular backplate that fits across the grip frame behind them, and are held in place by a screw.. The gun continued to be referred to as le Pistolet Browning. Markings were as follows:
For details on serial numbers, please refer to Anthony Vanderlinden’s book. He states that: “Production of the first commercial pistols was erratic and large gaps exist in the early serial number ranges.” Serial numbers began at 1, but many early pistols failed proof testing and were never completed. A total of approximately 724,550 M1900 pistols were manufactured. Production ended at the beginning of World War I in 1914, though sales had been considerably reduced by the introduction of the Model 1910, which went into production in 1912. The success of the M1899/1900 may have forced the Colt’s company to begin the manufacture of the first Colt Automatic Pistol in 1900. The finish of the M1900 was in rust blue or nickel plate. Early pistols had fire blued triggers like those on the Model 1899. Six different levels of engraving and gold inlay were available, as were mother-of-pearl and ivory grip plates. Nickeled pistols were given a black undercoat before plating, and the trigger, safety, and screws were left with this black finish. If the plating is worn off, the black undercoat should show through beneath it. For many years almost every article you read about the Model 1900 stated that it had been the gun used to assassinate Archduke Franz Ferdinand, starting World War I. The actual gun used was a Model 1910 FN Browning, but at the time the Model 1910 had only been out for 2 years and year model designations had not yet been adopted. The press reported that the assassination was performed with a Browning pistol, and the M1900 was the Browning pistol with which most of the world was familiar, so it was simply assumed to have been the gun used and the error was perpetuated for decades. The Model 1900 saw wide distribution throughout Europe. The Belgian war ministry placed an order for 10,000 guns in 1900, and it served as the standard sidearm for the Belgian military through World War I. The Austro-Hungarian empire also purchased the weapon; the exact quantity purchased is not known, but Vanderlinden states that 770 were in the military inventory of 1914. The gun was also widely used by German police. Don Maus has documented at least 62 Model 1900 FN pistols with German police markings. Many of these guns have safety markings in German, indicating that they were purchased under contract. The Model 1900 also saw use by police in Finland, as well as during various wars up to 1945. See Vanderlinden for details. Disassembly
When reinserting the breech block into the frame, pull the trigger to lower the sear. Field Test I finally found a Model 1900 FN Browning at a reasonable price--it has been reblued and doesn’t have the original grips, but the serial numbers match and it is fully functional. For a few years I had only seen them in pictures, and the actual gun was smaller than I had imagined from seeing them in photographs. The angle of the grip to the slide is about 10 degrees greater than perpendicular. Most modern guns have a grip angled a little more--about 15 degrees greater than perpendicular--which enables them to be pointed more naturally. Nevertheless, the M1900 feels good in my hand. I can get two fingers around the grip strap and my little finger wraps around the bottom of the grip quite naturally. I was astonished when four of the bullets from my first magazine went into the same hole (at about 25 feet)--if I were a better shot I believe I could shoot out the bullseye with this gun. The M1900 digested every kind of ammunition I put through it and never once failed to feed or eject. It is no wonder that it was an immediate success. * Berg resigned from FN on 28 April 1898, not long after his trip to Utah. He later worked for Flint & Company in Europe and also served as the business agent for the Wright brothers. According to Vanderlinden, he was still alive and living in Paris after World War II. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Copyright 2009-2021 by Ed Buffaloe. All rights reserved. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||



 Slide legends are roll stamped on the left side. There are
two legends found: FABRIQUE NATIONALE HERSTAL LIEGE and FABRIQUE NATIONALE HERSTAL LIEGE (BROWNING’S
PATENT). Apparently, these were interchangeable and both legends appear throughout production of the gun. The slides, frames, and breech blocks are all proofed with the Liege
Perron and an inspector’s proof, typically a star over a letter. Serial numbers are stamped on the right side of the frame, just in front of the ejection port, and are also stamped on the
right side of the slide and breech block. Serial numbers started at 1 and ran to 9999, after which they ran from A1 to A4500 (approximately).
Slide legends are roll stamped on the left side. There are
two legends found: FABRIQUE NATIONALE HERSTAL LIEGE and FABRIQUE NATIONALE HERSTAL LIEGE (BROWNING’S
PATENT). Apparently, these were interchangeable and both legends appear throughout production of the gun. The slides, frames, and breech blocks are all proofed with the Liege
Perron and an inspector’s proof, typically a star over a letter. Serial numbers are stamped on the right side of the frame, just in front of the ejection port, and are also stamped on the
right side of the slide and breech block. Serial numbers started at 1 and ran to 9999, after which they ran from A1 to A4500 (approximately).
